If your laptop is struggling to run Chrome, even with a fast internet connection, it’s possible that your CPU is overloaded and can’t keep up with the browser’s demands. In this case, you may want to try hardware acceleration, which is a feature that can either significantly improve performance or, in some cases, make things even worse. Here’s how to turn it on or off in Chrome.
What is Hardware Acceleration?
In simple terms, hardware acceleration is a feature that allows Chrome to offload certain tasks—like video rendering or running browser-based games—to your GPU instead of your CPU. In theory, this can relieve the burden on your CPU, thus resulting in better performance.
However, this isn’t always the case because sometimes it can cause crashes, lag, and super-fast battery drain. This stems from the fact that every GPU is different, and some don’t have the necessary drivers to support this feature efficiently.
How To Turn On/Off Hardware Acceleration in Chrome?
By default, hardware acceleration is enabled in Chrome. But if Chrome is lagging or glitchy, turning it off might help. Here’s how to do it:
- Open the Chrome browser.
- Click the three-dot menu in the top-right corner.
- Go to Settings.
- Navigate to the System tab.
- Toggle off Use hardware acceleration when available.
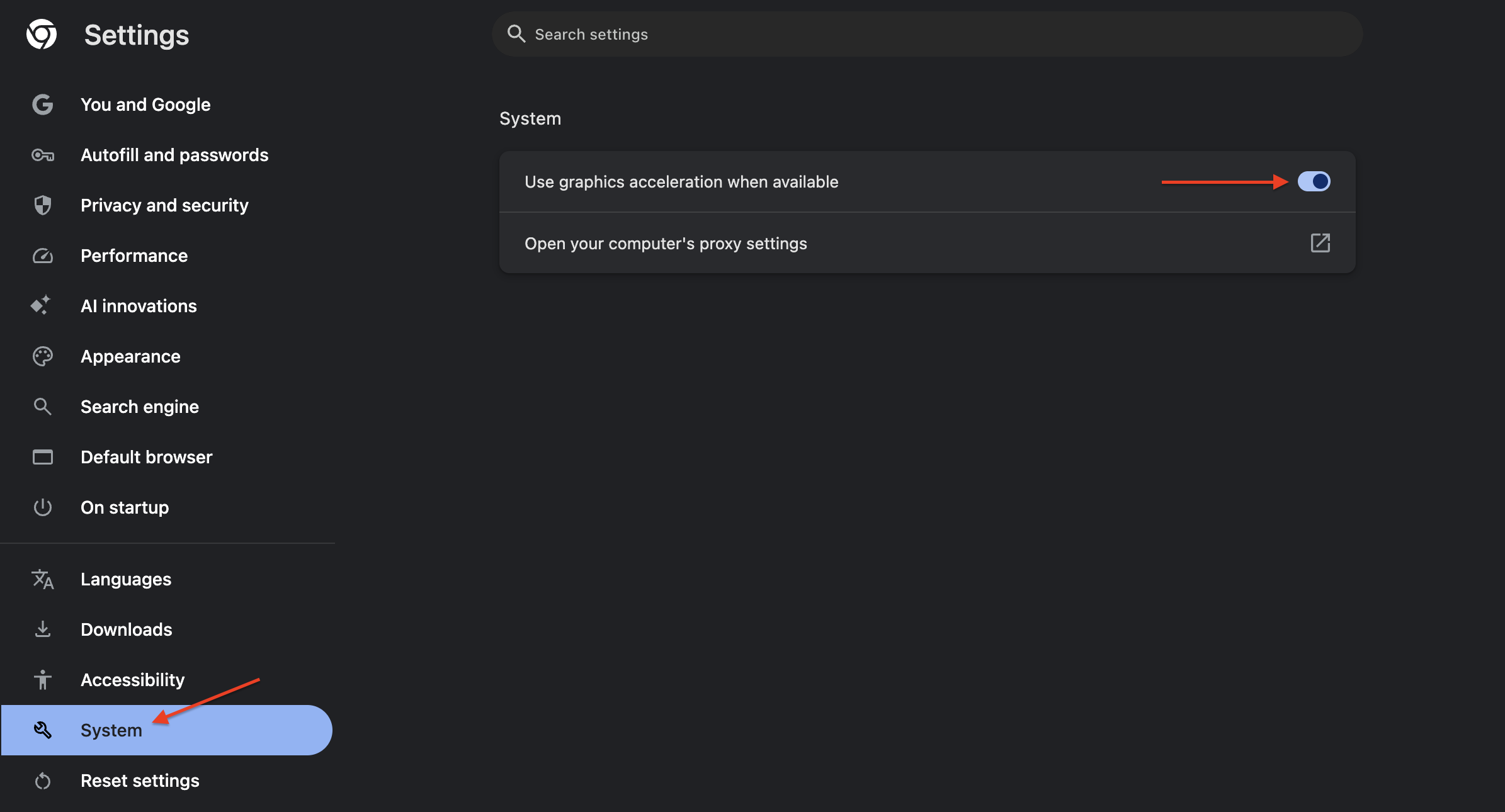
- Click Relaunch to restart Chrome and apply the change.
To check if hardware acceleration is disabled:
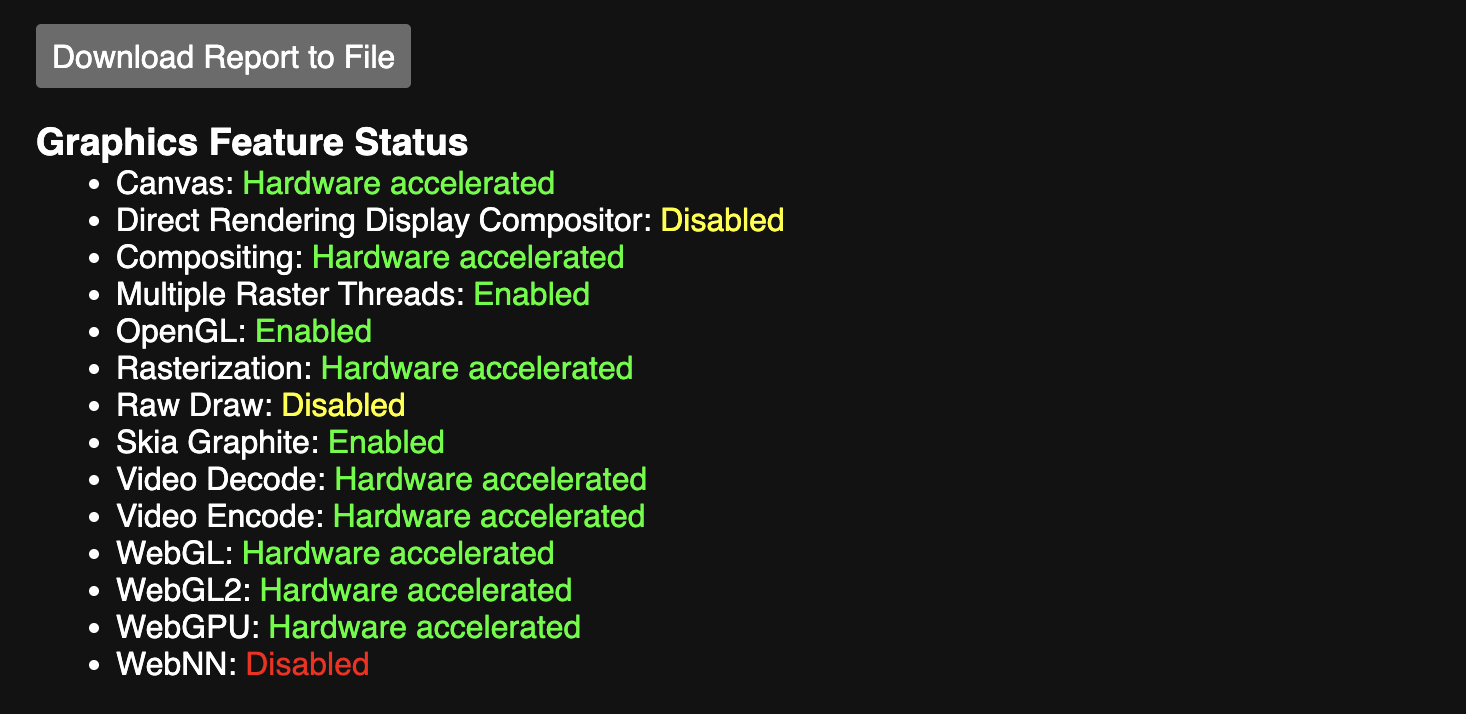
- Open Chrome and type
chrome://gpu/in the address bar. - If hardware acceleration is still active, you’ll see Hardware Accelerated written beside the tools in Graphics Feature Status.
Other Ways to Improve Chrome Performance
If hardware acceleration didn’t solve your problem, here are a few more tricks you can try:
- Clear browsing data: Cached files and cookies can slow Chrome down over time. To clear them, go to Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data.
- Disable unnecessary extensions: Extensions can consume system resources. Head to
chrome://extensions/and disable or remove the ones you don’t use. - Use Memory Saver: Chrome’s Memory Saver feature frees up RAM by sleeping inactive tabs, which can help improve speed and responsiveness.

